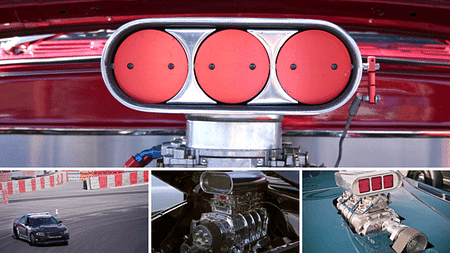
For those in the market for high-performance vehicles, supercharging and turbocharging are two common methods used to boost horsepower and torque. However, while both techniques involve compressing air before it enters the engine, they do so in different ways. This blog will explore the distinctions between supercharged cars and turbocharged cars, and help you determine which option is most suitable for your needs.
Supercharged Cars: Advantages and Disadvantages
Supercharging is the process of compressing air using a compressor powered by the engine. The compressor is usually driven by a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft, providing a continuous boost to the engine's performance throughout the rev range. Most commonly used in V8 and V6 engines, superchargers can be either roots-type or twin-screw.
Pros: Provides a linear power delivery due to a constant boost throughout the rev range. Offers better responsiveness than turbochargers, without needing exhaust gases to spin a compressor. Relatively easy to install, as no modifications are required to the exhaust system.
Cons: Can be expensive, as it requires a separate compressor and drive system.
Can increase fuel consumption significantly, making it less economical than turbocharging. Generates more heat than turbocharging, putting more stress on the engine.

Turbocharged Cars: Advantages and Disadvantages
Turbocharging is similar to supercharging, but it uses exhaust gases to compress air before it enters the engine. As exhaust gases leave the engine, they pass through a turbine that spins a compressor, compressing air before it enters the engine. Turbochargers are commonly used in four-cylinder engines and can be either single-turbo or twin-turbo.
Pros: More efficient than supercharging, as it uses exhaust gases to spin a compressor. Can provide more power and torque than supercharging, especially in twin-turbo systems. More economical than supercharging, as it doesn't require as much power from the engine to provide a boost.
Cons: Can experience more lag than supercharging, due to the need for exhaust gases to spin the compressor. Generates more heat in the exhaust system, requiring modifications to prevent damage. More complex to install, as it requires modifications to the exhaust system.
Final Thoughts
When deciding between supercharged and turbocharged cars, it's essential to weigh the pros and cons of each. Supercharging offers better responsiveness and ease of installation, but it can be more expensive and increase fuel consumption. Turbocharging is more efficient, provides more power, and is more economical, but can experience lag and requires more complex installation. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual needs and preferences.